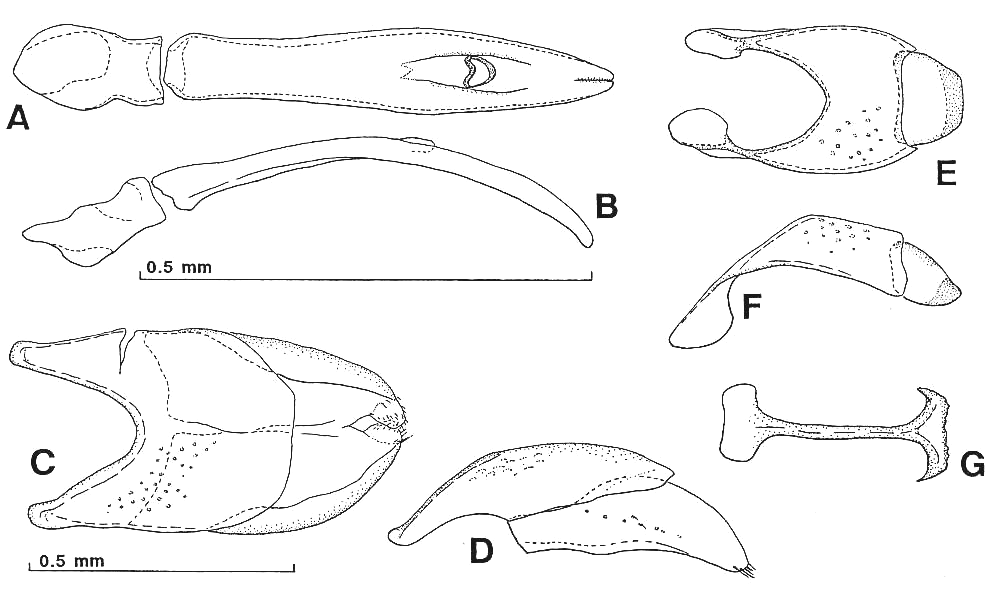
Description. Body length, PPL, 2.13, PEL, 1.90. Width, 1.52. Biometric data as follows: APW 0.67, PPW 1.43, PL 0.76, EW 1.52, ProW 0.88, ProL 0.23, PTL 0.53, MSTL 0.55, MTTL 0.61. Body oval, convex, not shining and black; legs and antennae dark reddish brown.
Frontal stria of head (Fig. 148B) rudimentary behind apical angle (but it seems that the state of the only specimen available is not complete, with dermal structures defaced to some extent). Disk of front with rudimentary transverse rugae.
Pronotal sides (Fig. 148A, 149) convergent on basal one-sixths, thence strongly arcuate and convergent to apices. Apical angles round. Marginal stria carinate and complete laterally, the apical portion broadly interrupted behind head. Disk coarsely and densely punctate, the punctures becoming more rugose in lateral region and absent mediobasally; base with two or three transverse rows of large and oblong punctures, the rows being broadest at middle and becoming narrower laterally.
Marginal epipleural stria complete and clearly impressed. Marginal elytral stria complete, broadly impressed in the basal third, the apical end extending inwards, reaching to near lateral fourth of posterior margin of elytron. External subhumeral stria absent. Internal subhumeral stria impressed on median third. Oblique humeral stria present on basal third, the area around the stria with several short rugae. First dorsal elytral stria completely present, but shortly reduced on apical eighth. Second to 4th dorsal striae well impressed on basal half, the basal end of 4th extending inwards and united with the base of sutural stria. Sutural stria completely impressed. Surface of elytra smooth on basal half, and densely covered with coarse and deep punctures, which are often united to form longitudinal rugae; extreme apex of elytron and flank sparsely and finely punctate.
Propygidium densely covered with coarse and round punctures, which become finer and sparser towards the base, but mostly are separated by their diameter. Pygidium densely covered with coarse punctures, which are a little smaller than those of the propygidium and separated by one-thirds to half their diameter; on the apex the punctures becoming finer and sparser.
Anterior margin of median portion of prosternum (Fig. 148C) weakly obtuse-angulate. Preapical foveae deeply and distinctly present. Keel narrow, strongly compressed, its anterior apex truncate. Descending lateral striae carinate and convergent to apex, but their apical portions nearly parallel. Carinal striae completely impressed, divergent apically and basally, the anterior ends united with descending lateral striae. Lateral side of keel coarsely punctate, the punctures being separated by their own diameter to twice the dimeter.
Anterior margin of mesosternum feebly emarginate, its marginal stria carinate and complete. Disk of mesosternum smooth. Meso-metasternal suture lightly impressed, accompanied with a parallel coarsely crenated line. Intercoxal disk of metasternum smooth. Lateral metasternal stria well impressed and carinate, extending obliquely and posteriorly and reaching near hind coxa. Lateral disk densely covered with coarse, round and shallow punctures on basal half, the punctures gradually becoming smaller and sparser; impunctate along the lateral stria and on posterior half of the disk. Metepisternum densely and coarsely punctate.
Intercoxal disk of 1st abdominal sternum smooth, and completely striate on each side.
Protibia with 6 spinules on outer margin, its apical outer angle bearing two large denticles.
Male genitalia as shown in Fig. 150.
Specimens examined. Holotype, 1Åâ, Mount Akan, Kushiro, Hokkaidô, 5/viii/1918, M. Suzuki leg. (Kyûshû University Coll.).
Distribution. Japan (Hokkaidô).
Remarks. The aedeagus of this species is similar in shape to that of Hypocaccus (Hypocaccus) speculum (Schmidt) (Kryzanovskij and Reichardt, 1976: 225, fig. 443), but the punctuation of elytra is quite different.
Hypocaccus akanensis resembles surperficially H. sinae but can easily be distinguished by the smaller body and the sutural stria being not united with marginal elytral stria.
